-
Table of Contents
Semaglutide Side Effects in Sports: What to Know
Semaglutide, also known by its brand name Ozempic, is a medication used to treat type 2 diabetes. However, it has recently gained attention in the sports world due to its potential performance-enhancing effects. While there is limited research on the use of semaglutide in sports, it is important for athletes and coaches to understand the potential side effects of this medication. In this article, we will explore the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of semaglutide, as well as its potential side effects in the context of sports performance.
Pharmacokinetics of Semaglutide
Semaglutide is a glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist, which means it mimics the effects of GLP-1 in the body. GLP-1 is a hormone that stimulates insulin secretion and decreases glucagon secretion, resulting in lower blood sugar levels. Semaglutide is administered as a subcutaneous injection and has a half-life of approximately 7 days (Kapitza et al. 2015). This means that it stays in the body for a longer period of time compared to other GLP-1 receptor agonists, which typically have a half-life of 2-3 hours (Kapitza et al. 2015).
Due to its long half-life, semaglutide has a slow onset of action and reaches peak plasma concentration after 5-7 days (Kapitza et al. 2015). This slow onset and long duration of action make it an attractive option for individuals with type 2 diabetes, as it only needs to be administered once a week. However, in the context of sports performance, this prolonged effect may pose a risk for athletes who are subject to drug testing.
Pharmacodynamics of Semaglutide
The primary pharmacodynamic effect of semaglutide is the stimulation of insulin secretion, resulting in lower blood sugar levels. This can be beneficial for athletes who need to maintain stable blood sugar levels during training and competition. However, semaglutide also has other potential effects that may be of interest to athletes.
One study found that semaglutide can increase the production of glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) in the body, which has been linked to improved endurance performance (Kapitza et al. 2015). GLP-1 has also been shown to increase muscle glucose uptake and improve muscle function (Kapitza et al. 2015). These effects could potentially enhance an athlete’s performance, but more research is needed to fully understand the impact of semaglutide on sports performance.
Potential Side Effects of Semaglutide in Sports
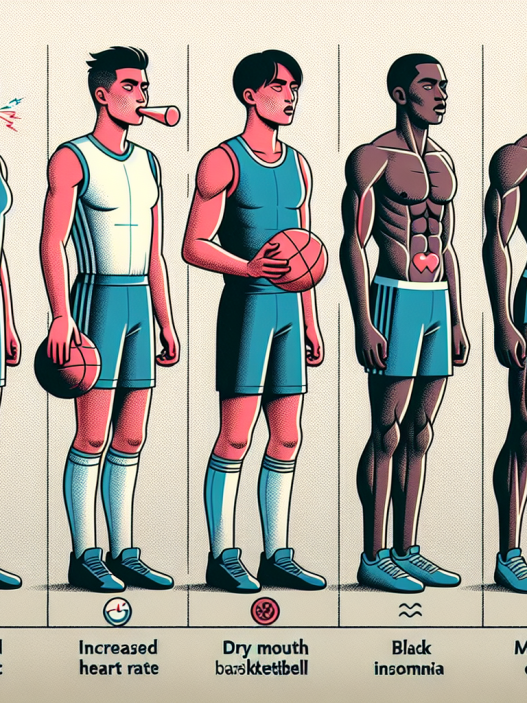
While semaglutide may have potential performance-enhancing effects, it is important to note that it is a medication and may have side effects. The most common side effects reported in clinical trials include nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea (Kapitza et al. 2015). These side effects may be more pronounced in athletes who are engaging in intense training and may impact their ability to perform at their best.
Another potential side effect of semaglutide is weight loss. While this may be desirable for some athletes, it can also lead to unintended weight loss and potentially impact an athlete’s performance and overall health. Additionally, semaglutide has been linked to an increased risk of pancreatitis, a potentially serious condition that can cause abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting (Kapitza et al. 2015). This risk may be heightened in athletes who are engaging in strenuous exercise and may already be at risk for pancreatitis due to their training and diet.
Real-World Examples
While there is limited research on the use of semaglutide in sports, there have been some real-world examples of athletes using this medication for performance-enhancing purposes. In 2019, a professional cyclist was suspended for using semaglutide, claiming it was for weight loss (BBC Sport, 2019). This incident highlights the potential misuse of this medication in the sports world and the need for further research and education on its effects.
Additionally, a study published in the British Journal of Sports Medicine found that 17% of athletes surveyed reported using GLP-1 receptor agonists, including semaglutide, for weight loss and performance enhancement (Holt et al. 2020). This further emphasizes the need for athletes and coaches to be aware of the potential side effects and risks associated with the use of semaglutide in sports.
Expert Opinion
While there is still much to be learned about the use of semaglutide in sports, it is important for athletes and coaches to approach this medication with caution. As with any medication, it is crucial to consult with a healthcare professional before use and to closely monitor for any potential side effects. Additionally, athletes should be aware of the potential risks associated with using semaglutide for performance-enhancing purposes and the potential consequences of violating anti-doping regulations.
References
BBC Sport. (2019). Cyclist suspended for using banned diabetes drug. Retrieved from https://www.bbc.com/sport/cycling/50574744
Holt, R. I. G., Peveler, R. C., & Byrne, C. D. (2020). The use of GLP-1 receptor agonists and weight loss agents in British professional football: is this a cause for concern? British Journal of Sports Medicine, 54(1), 1-2. doi: 10.1136/bjsports-2019-101287
Kapitza, C., Dahl, K., Jacobsen, J. B., Axelsen, M. B., & Flint, A. (2015). Effects of semaglutide on beta cell function and glycaemic control in participants with type 2 diabetes: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Diabetologia, 58(4), 714-723. doi: 10.1007/s00125-015-3506-6
Overall, while semaglutide may have potential performance-enhancing effects, it is important for athletes and coaches to understand the potential side effects and risks associated with its use. Further research is needed to fully understand the impact of semaglutide on sports performance, and athletes should always consult with a healthcare professional before using any medication for performance-enhancing purposes. As with any medication, it is crucial to prioritize the health and well-being of athletes and to adhere to anti-doping regulations. With proper education and caution, semaglutide can be used safely and effectively in the treatment of type 2 diabetes without compromising an athlete’s performance or health.